Hernia in Children

What is the meaning of Hernia in Children?
A hernia is a defect or weakening in the abdominal wall that allows tissue (usually intestines) or fat to protrude and form a lump. Hernias are more common in adults, although they can also develop in children and infants.
Causes of Hernia in Children
Openings in the abdominal wall are common in newborns and usually close before or immediately after birth. Hernias commonly occur in babies and children when these openings do not close properly, enabling the intestines or other organs to push through. Hernias can appear shortly after birth or years later during childhood.
A variety of factors can contribute to hernias in children, including:
- Congenital defects: Some children are born with weak abdominal muscles or tissues, which can lead to hernias
- Coughing, crying, straining, or other behaviours that put pressure on the abdominal wall might create increased abdominal pressure
- Can be caused by a severe accident, such as a fall or a hit to the abdomen.
Symptoms of Hernia in Children

It is important for parents to be able to recognise the signs of a hernia in young children, particularly infants and toddlers, who are unable to express their discomfort most of the time. The following are the most common symptoms of a hernia in children:
- A visible lump or bump in the affected area
- Pain or discomfort in the affected area
- Swelling or redness in the affected area
- Nausea or vomiting
- Constipation
If your child presents any of the symptoms listed above, seek medical assistance with your child’s doctor to avoid potentially serious complications.
Types of Hernia in Children
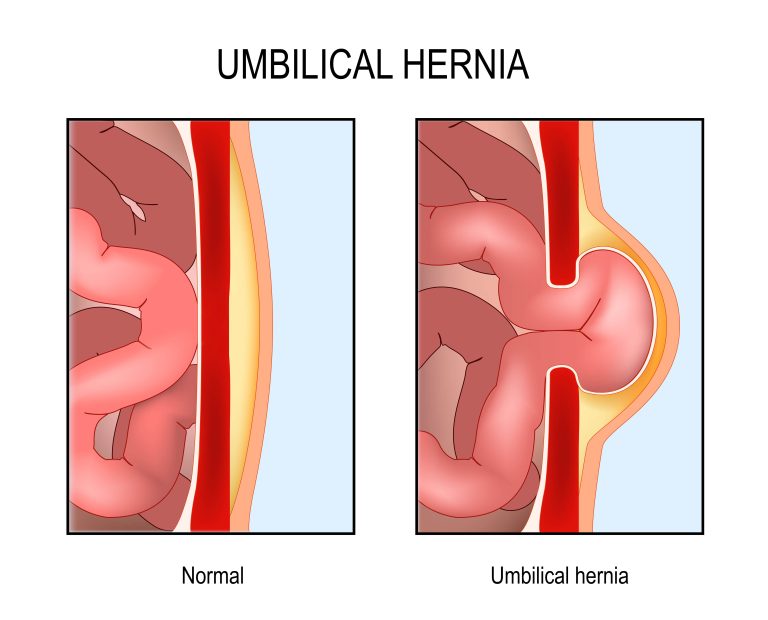
The most common types of hernias in children and babies are inguinal (groin) and umbilical (belly button).
- Inguinal hernias occur when a part of the intestine protrudes through the inguinal canal, a weak spot in the lower abdominal wall near the groin.
- Umbilical hernias are common in newborns and infants. It happens when a part of the intestine protrudes through the umbilicus (belly button).
Diagnosis and Treatment of Hernia in Children
A hernia in a child is often diagnosed by a physical exam in which the doctor feels for a lump or bulge in the affected area. An X-ray, CT scan, or ultrasound may be required in some circumstances to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for a hernia in a child is determined by the size and location of the hernia, as well as the child’s overall health. Hernias can be managed in certain conditions with lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise to relieve pressure on the affected area. In other circumstances such as inguinal hernias and some umbilical hernias, surgery may be required to correct the hernia and avoid major health complications.
What is a Hernia Surgery?
A hernia surgery (also known as hernia repair surgery) in a child is normally performed under general anaesthesia and is regarded as a safe and effective operation. The two surgical techniques used in hernia surgery for children are:
- Open Surgery: A small incision will be made under or through the belly button for umbilical hernias, and in the groin for inguinal hernias
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Requires a number of tiny incisions in the abdominal and groin areas.
Following the surgery, the child may need to rest and heal before returning to everyday activities.
Schedule an appointment with our Paediatric Surgeon to understand more about the risks and benedits of a hernia surgery.



