Hormones play a crucial role in regulating various functions in our body, from metabolism and mood to reproductive health and energy levels. As we age, hormonal changes can impact our well-being in different ways. Understanding these shifts and seeking timely medical support can help you maintain optimal health at every stage of life.
What are Hormones?
Hormones are the body's chemical messengers, produced by the endocrine system1, that help control how we grow, feel, and function. The endocrine system, made up of glands such as the thyroid, adrenal glands, and pancreas, releases hormones that regulate2 your:
- metabolism,
- energy levels,
- growth and development,
- body defences,
- emotions, and
- reproductive health.
Hormones play different roles in keeping the body functioning properly. Here are some of the key types of hormones:
- Metabolic Hormones: Regulate energy and blood sugar levels.
Examples: Insulin (lowers blood sugar), Glucagon (raises blood sugar), Thyroid hormones (control metabolism). - Stress and Sleep Hormones: Help the body respond to stress and regulate sleep patterns.
Examples: Cortisol (stress response), Melatonin (controls sleep cycles). - Reproductive Hormones: Affect growth, development, and fertility.
Examples: Oestrogen and Progesterone (female reproductive health), Testosterone (muscle mass, libido, and mood in both genders). - Growth and Development Hormones: Support body growth and maintenance.
Examples: Growth Hormone (muscle and bone development), Prolactin (stimulates milk production). - Mood and Emotional Regulation Hormones: Influence mood, motivation, and social bonding.
Examples: Serotonin (regulates mood and sleep), Dopamine (pleasure and motivation), Oxytocin (social bonding and relationships).
Why Hormonal Health Matters
Having a clear understanding of these hormones and how they function allows individuals to make informed choices about their lifestyle, diet, and healthcare, ensuring better hormonal balance and overall well-being.
When left unchecked, hormonal imbalances can contribute to serious health conditions such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which may lead to complications like infertility, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic dysfunction. Additionally, hormonal fluctuations can impact mental health, contributing to anxiety, depression, and mood instability, ultimately affecting emotional resilience and daily life.
Taking proactive steps to support hormonal health through regular check-ups, stress management, and a balanced diet can help prevent these complications and improve quality of life.
Signs of Hormonal Imbalances
Recognising the symptoms of hormonal imbalance early can help in seeking timely medical intervention. Some common signs include:

Unexplained Weight Changes
Sudden weight gain or loss without changes in diet or exercise could indicate thyroid health issues, insulin resistance, or adrenal imbalances.

Chronic Fatigue
Persistent exhaustion, even after a full night's sleep, may suggest endocrine disorders such as thyroid dysfunction or adrenal fatigue.

Mood Swings and Anxiety
Frequent mood changes, depression, or heightened anxiety can be linked to imbalances in cortisol, oestrogen, or testosterone.

Irregular or Painful Periods
Inconsistent menstrual cycles, heavy bleeding, or extreme pain may indicate conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or perimenopause.

Sleep Disturbances
Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep might be associated with imbalances in melatonin, cortisol, or sex hormones.

Skin and Hair Changes
Excessive acne, dry skin, hair thinning, or sudden hair loss can be signs of hormonal health issues related to androgens or oestrogen levels.

Low Libido and Sexual Dysfunction
A decline in sexual desire or performance may be associated with hormonal imbalances affecting testosterone, oestrogen, or progesterone.

Digestive Issues
Bloating, constipation, or sudden digestive discomfort can be linked to gut microbiome changes caused by hormonal fluctuations.
By actively managing hormonal health through lifestyle adjustments, medical intervention, and routine screenings, individuals can enhance their overall quality of life and prevent long-term complications.
If you experience any of these symptoms persistently, consulting an endocrinologist in Singapore can help diagnose and manage underlying hormonal health concerns.
Hormonal Health Through the Life Stages
Hormonal fluctuations are a natural part of life, influencing everything from growth and development to metabolism and emotional well-being. While these changes are expected, they can sometimes lead to imbalances that affect daily life.
Understanding how hormones shift at different stages and adopting strategies to maintain balance can support overall health and well-being. Below, we explore the key hormonal changes that occur during different life stages and how to manage them effectively.
Adolescence (10–19 years): Navigating Puberty and Growth
Puberty marks a significant hormonal shift as the body prepares for adulthood. The pituitary gland signals the release of key hormones like oestrogen, progesterone, and testosterone, triggering physical and emotional changes. During this phase, rapid physical and emotional changes occur, driven by hormones such as oestrogen, progesterone, and testosterone.
These hormonal changes lead to various physical developments:
- Boys: Increased testosterone levels result in growth spurts, development of body and facial hair, deepening of the voice, and increased muscle mass.
- Girls: Elevated oestrogen and progesterone levels lead to breast development, the onset of menstrual cycles, and the accumulation of body fat in areas like the hips and thighs.
Additionally, these hormonal shifts can influence mood, leading to heightened emotions, increased appetite, and changes in sleep patterns. While these changes can be challenging, they are a natural part of development and can be managed with a healthy lifestyle, balanced nutrition, and proper self-care.
Tips for Managing Hormonal Health in Adolescence:
- Maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals is crucial for healthy development and growth. Nutrients such as zinc and vitamin A help with skin health, while calcium supports strong bones.
- Regular physical activity can help regulate mood and hormonal balance, reducing stress and promoting overall well-being.
- Seeking medical advice for irregular or painful menstrual cycles ensures that any underlying hormonal health issues, such as PCOS, are identified and managed early.
Adulthood (20–39 years): Maintaining Hormonal Balance
In adulthood, a variety of lifestyle factors, including diet, stress, and sleep patterns, play a significant role in maintaining hormonal health.
Many adults struggle with hormone-related concerns, such as thyroid disorders, fertility issues, and metabolic imbalances, which can affect energy levels, mood, and overall well-being. For example, long-term stress can lead to cortisol dysregulation, increasing the risk of weight gain, anxiety, and even heart disease. Poor sleep habits and irregular eating patterns can contribute to insulin resistance, impacting metabolism and raising the risk of conditions like Type 2 diabetes.
The endocrine system regulates metabolism, reproductive health, and stress response, making it essential to support hormonal balance through a proactive approach that includes regular health check-ups, balanced nutrition, stress management, and maintaining an active lifestyle.
Tips for Managing Hormonal Health in Adulthood3:
- Eating a diet high in fibre, lean proteins, and healthy fats supports hormonal regulation by stabilising blood sugar levels and promoting gut health.
- Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule is essential for balancing cortisol and melatonin, which impact energy levels, mood, and hormonal function.
- Regular health check-ups, including screenings for thyroid health, insulin resistance, and reproductive hormones, can help detect early signs of hormonal imbalances.
- Prioritising stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can help regulate cortisol levels and reduce the risk of hormonal disorders.
Midlife and Beyond (40+ years): Menopause, Andropause, and Aging
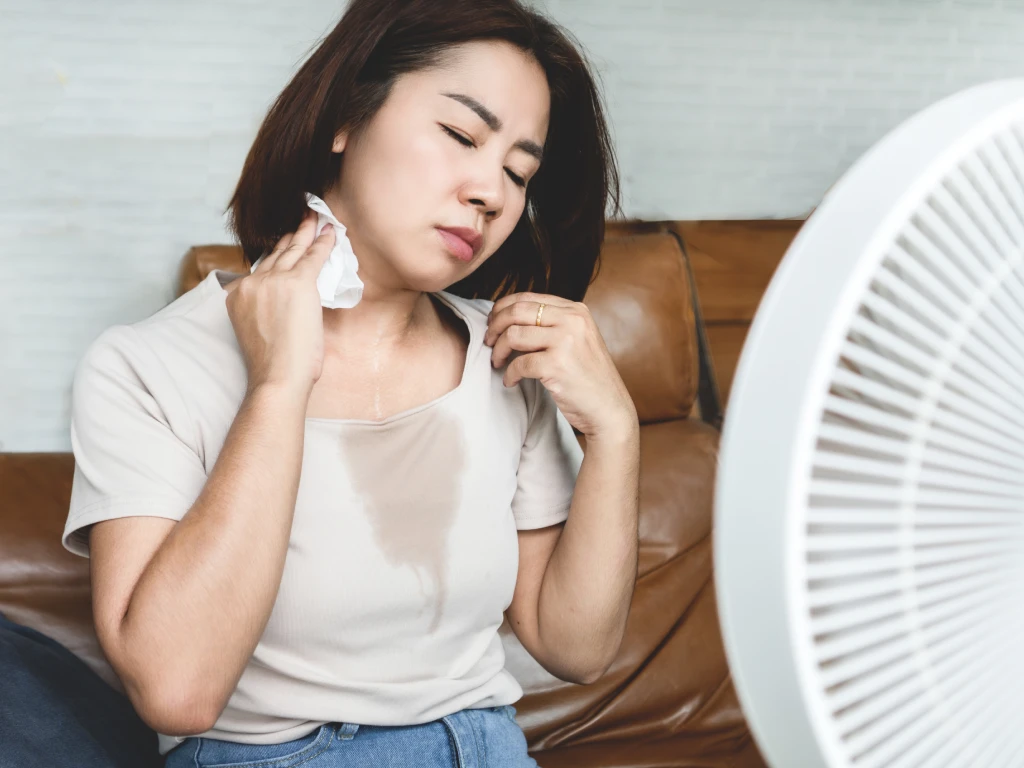

As individuals enter their 40s and beyond, significant hormonal changes occur due to ageing. Both men and women experience shift that affect their metabolism, energy levels, mood, and overall health. While these transitions are a natural part of ageing, they can profoundly impact physical and mental well-being.
- Menopause4: For women, menopause typically occurs between ages 45-55, leading to a decline in oestrogen and progesterone. This hormonal shift results in common symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and changes in metabolism, making it harder to maintain a healthy weight. Additionally, oestrogen plays a key role in bone health, and its decline increases the risk of osteoporosis. Women may also experience vaginal dryness, decreased libido, and increased susceptibility to heart disease due to changes in cholesterol levels and blood vessel function.
- Andropause5: Men experience andropause, a gradual decline in testosterone levels, which can lead to lower energy levels, reduced muscle mass, and diminished libido. Testosterone also influences mood, and its reduction may contribute to irritability, depression, or difficulty concentrating. Many men also experience a slower metabolism, which can lead to weight gain and an increased risk of cardiovascular issues. Sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or reduced sleep quality, are also commonly reported during this stage of life.
Beyond the immediate symptoms, the long-term effects of these hormonal shifts are significant. Both men and women may experience changes in cardiovascular health, as hormonal imbalances can contribute to increased cholesterol levels and higher blood pressure, leading to greater risks of heart disease.
Tips for Managing Hormonal Health in Midlife and Beyond6:
- A diet rich in healthy fats, fibre, and lean proteins supports metabolic health and stabilises energy levels. Incorporate foods rich in phytoestrogens (such as soy and flaxseeds) to help balance hormone levels. Reduce processed foods and refined sugars to support metabolic health.
- Engage in regular strength training and weight-bearing exercises to maintain muscle mass, support bone density, and enhance overall energy levels.
- Establish a consistent bedtime routine and limit screen time before bed to improve melatonin production and reduce sleep disturbances.
- Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to regulate cortisol levels and reduce mood swings.
- Stay Hydrated and Support Skin Health: Drink plenty of water and use moisturisers to counteract skin dryness caused by declining oestrogen levels.
When to See an Endocrinologist
If you're experiencing persistent symptoms like extreme fatigue, unexplained weight changes, irregular periods, or difficulty managing chronic conditions, it may be time to see an endocrinologist in Singapore.
At Nobel Diabetes, Thyroid and Endocrine Centre, our experienced specialists, led by Senior Consultant Endocrinologist Dr. Nitish Mishra, provide comprehensive diagnostics and personalised treatment plans tailored specifically to your hormonal health needs. Our centre specialises in managing diabetes (including Type 1, Type 2, gestational diabetes, and insulin pump management), thyroid disorders (hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, thyroid nodules, thyroid cancer), and hormonal imbalances such as adrenal diseases, hypogonadism, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), growth and delayed puberty, and pituitary disorders.
Access personalised treatment options and lifestyle modifications tailored to individual needs at Nobel Diabetes, Thyroid and Endocrine Centre.
References:
- Dorwart L. What Do Hormones Do in Children, Men, and Women? Verywell Health, 2025.
- Huizen J. What to Know About Hormonal Imbalances. Medical News Today. Updated 2024.
- BodyLogicMD Medical Review Board. Lifestyle Factors and Hormone Levels. BodyLogicMD. 2024.
- Menopause — Symptoms & Causes. Mayo Clinic.
- Andropause or Male Menopause: What Causes It? HealthXchange.
- Lang A. Medically reviewed by Biggers A., M.D., MPH. How To Balance Your Hormones Naturally. Healthline. Updated 2024.